At enVgrow, we specialize in intelligent gas delivery and life safety monitoring. One of the most important elements of our system is the sensors. Sensors are the eyes and ears of the control system. They take in information and send it to the controller, which makes the decision on what component needs to be adjusted to achieve the desired set point. Without an accurate sensor, the controller cannot make adjustments effectively.
Carbon dioxide detectors are manufactured, tested and rated on a sensitivity range and the level of sensitivity required depends upon the conditions and what is being measured. Carbon dioxide detectors measure CO₂ in parts per million (or PPM) and there are different ranges of detection per meter based upon its intended use.
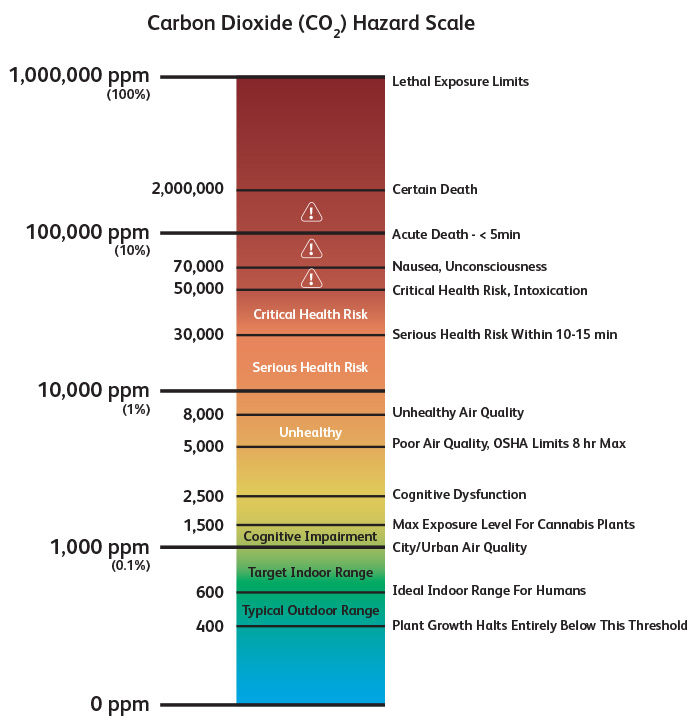
A CO₂ sensor installed as part of an HVAC system will measure indoor CO₂ saturation levels. Indoor levels usually range from 350PPM to about 450PPM, with a maximum comfort level being about 1500PPM. Outdoor CO₂ air saturation is about 400PPM in rural areas, and 1000PPM in urban areas. An indoor climate with a CO₂ saturation of about 1500PPM is considered to be an enriched environment. Sensors used in this application must be able to quickly detect saturation levels. More importantly, they need to provide accurate readings so the system can alarm if CO₂ levels become dangerous.
OSHA states that over an eight hour exposure period, 5000PPM is the maximum safe saturation level. enVgrow’s CO₂ sensors are extremely sensitive and provide precision readings on higher and wider ranges of CO₂ levels, not just for efficient enrichment, but for life safety. Through a required alarm system, occupants are immediately alerted through audio-visual alarms (in addition to SMS) if gas levels become greater than 5000PPM.
Without a correct reading, the controller may make unnecessary adjustments, resulting in unsatisfactory results. Awareness of your sensor’s accuracy is critical when diagnosing any issues. Sensor accuracy is determined by frequently testing against a reference gas with a known PPM value. All sensor readings are recorded. The range of readings defines the accuracy of the sensor. The readings can be expressed as a ± (plus-minus) value in parts per million, as a percentage of the measured value, or a combination of both.
For example, if a sensor is tested with a gas of a known quantity, (let’s use 5000PPM) and the sensor reads between 4950PPM and 5050PPM, the reading would be expressed as ± 50PPM or 2% (100/5000). When sensors consistently perform within their preset ranges, they are recognized as accurate. enVgrow takes pride in providing sensors that are both accurate and reliable.
Many factors influence sensor inaccuracy. Most inaccuracies are commonly caused by the following:
- The method of sensor calibration (field calibration versus auto-calibration)
- The frequency of calibration
- The quality of manufacturing
- Environmental factors (such as exposure to water and airborne pollutants)
Oftentimes, lesser sensors are employed by means of trying to save on cost. Initially, it may seem like a good idea to go with low cost hardware. Unfortunately, these cost-saving strategies do not usually work as planned and have resulted in damage to facility and/or products, total loss of crops, injured employees and noncompliance. At enVgrow, we know the quality of sensors is paramount to the safe, and effective operation of your facility. We have partnered with some of the best companies in the world, to offer our clients the highest quality of hardware available.
Are you worried or wondering about the accuracy of your sensors? Contact us today! We are happy to schedule a facility evaluation and diagnosis, and can advise on how to optimize your facility.